Talking about People through Dance - Pina Bausch Biography
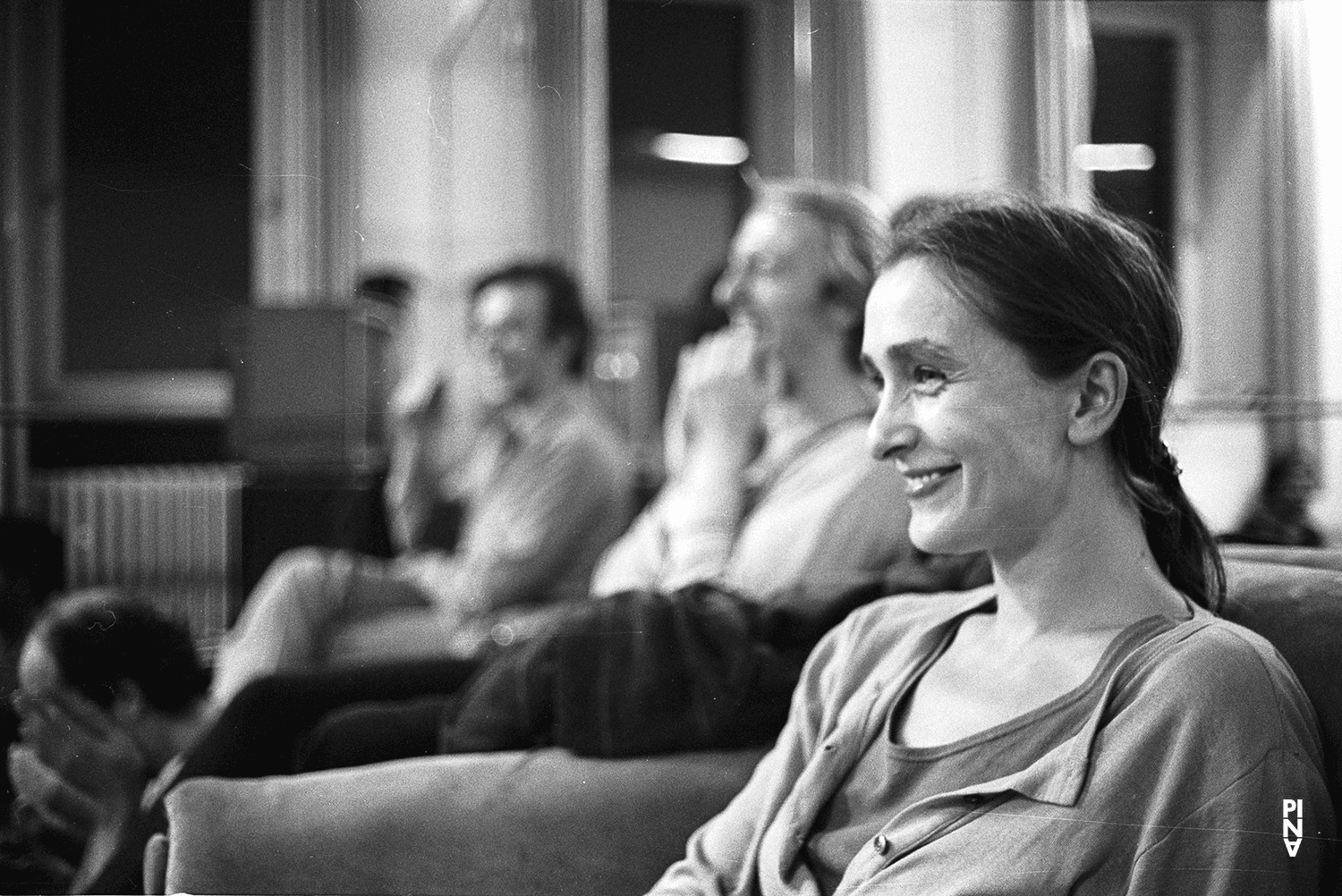
Pina Bausch was born 1940 in Solingen and died 2009 in Wuppertal. She received her dance training at the Folkwang School in Essen under Kurt Jooss, where she achieved technical excellence. Soon after the director of Wuppertal's theatres, Arno Wüstenhöfer, engaged her as choreographer, from autumn 1973, she renamed the ensemble the Tanztheater Wuppertal. Under this name, although controversial at the beginning, the company gradually achieved international recognition. Its combination of poetic and everyday elements influenced the international development of dance decisively. Awarded some of the greatest prizes and honours world-wide, Pina Bausch is one of the most significant choreographers of our time.
She was born in 1940 in Solingen as Philippine Bausch; under her nickname Pina she was later to gain international standing from nearby Wuppertal with her dance theatre. Her parents ran a restaurant in Solingen attached to a hotel where, along with her siblings, Pina helped out. She learned to observe people, above all the fundamental things which drive them. The atmosphere of her early childhood seems to find an echo later in her pieces; music is heard, people come and go, and talk of their yearning for happiness. Yet her early experience of the war is also reflected in the pieces, in sudden outbursts of panic, fear of an unnamed danger.
Having already danced in the Solingen children's ballet, at fourteen Pina Bausch began studying dance with Kurt Jooss at the Folkwang School in Essen. Jooss was a significant proponent of pre- and post-war German modern dance which had freed itself from the shackles of classical ballet. In his teaching, however, Jooss sought to reconcile the free spirit of the dance revolutionaries with the fundamental rules of ballet. The young dance student Bausch thus acquired techniques for free creative expression as well as the command of a clear form. The proximity of the other arts taught at the Folkwang School, including opera, music, drama, sculpture, painting, photography, design, was also an important influence on her, reflected later in the form of a wholly open approach to the media in her work as a choreographer.
In 1958 Pina Bausch was awarded the Folkwang Leistungspreis and, armed with a grant from the Deutschen Akademischen Austauschdienst (German Academic Exchange Service: DAAD) she spent a year as 'Special Student' at the Juilliard School of Music in New York. The city was seen as a dance Mecca, where classical ballet was being reinvented thanks to George Balanchine and modern dance further developed. Pina Bausch's teachers included Antony Tudor, José Limón, dancers from Martha Graham's company, Alfredo Corvino and Margret Craske. As a dancer she worked with Paul Taylor, Paul Sanasardo and Donya Feuer. She took every opportunity to see performances and absorbed all the various tendencies. Enthused by the diversity of cultural life in New York, she remained for a further year. Now, however, she was obliged to finance her stay and found employment with Antony Tudor at the Metropolitan Opera. In her later work her affinity to opera and her respect for musical tradition was to play a equal role to, for instance, her love of jazz. The distinction between 'serious' and 'popular' music, still firmly upheld in Germany, was of no significance to her. All music was afforded the same value, as long as it expressed genuine emotions.
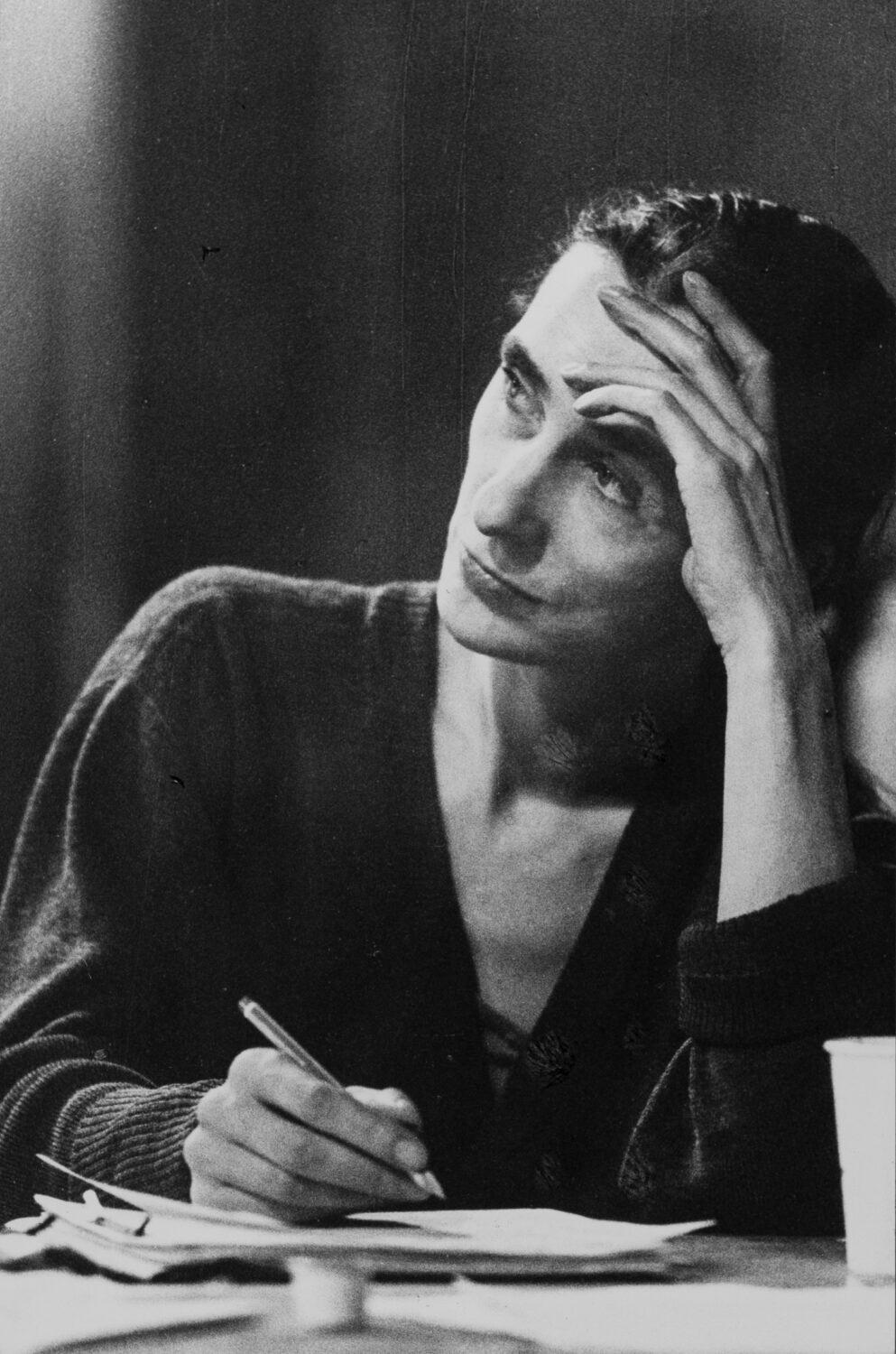
Two years after she had left for New York Kurt Jooss asked her to return to Essen. He had succeeded in re-invigorating the Folkwang Ballet, subsequently re-named the Folkwang Tanzstudio. Pina Bausch danced in works by Jooss, both old and new, as well as assisting him with choreography. As the Folkwang Tanzstudio needed new pieces, she began to choreograph independently and created works such as Fragment or Im Wind der Zeit, for which she was awarded first prize at the International Choreographic Workshop of 1969 in Cologne. She created her first works in Wuppertal as guest choreographer, performed with members of the Folkwang Tanzstudio: Aktionen für Tänzer in 1971 and the Tannhäuser Bacchanal in 1972. In 1973 the director of the Wuppertal theatres Arno Wüstenhöfer appointed her head of the Wuppertal Ballet, which she soon renamed the Tanztheater Wuppertal. The description Tanztheater, or dance theatre, originally used by Rudolf von Laban in the 1920s, is a statement of intent; it stands for an emancipation from mere balletic routines and the complete freedom to chose one's means of expression and Pina Bausch now developed several new genres in quick succession. With the two Gluck operas Iphigenie auf Tauris (1974) and Orpheus und Eurydice (1975) she created the first dance operas. In 1974, with I'll Do You In..., she entered the frivolous world of popular songs, while Come Dance with Me used old German folk songs and Renate wandert aus (Renate Emigrates) played on the clichés of operetta (both 1977). Her 1975 choreography for Igor Stravinsky's Le Sacre du printemps was to become a milestone; the emotional force and unmediated physicality of the piece became trademarks of her work. From Kurt Jooss she had learned 'honesty and precision'. Bausch demonstrated both these values, unleashing dramatic energy of a kind never seen before. In the early Wuppertal years this lead to consternation among press and public. The confrontation with the true motives behind human movements was painful. To many people the grief and despair evoked in 1977's Bluebeard. While listening to a tape recording of Bela Bartók's opera "Duke Bluebeard's Castle" in which passages of the music are repeated relentlessly, felt like torture. But along with her talent for drama Pina Bausch also demonstrated a sense of humour right from the start, seen for instance in her Brecht/Weill double-bill The Seven Deadly Sins and Don't Be Afraid of 1976. The second part, collaged freely together, with both men and women wearing female clothes as Bausch plays with entrenched gender-role conventions, is both entertaining and funny.
In 1978 Pina Bausch changed her working methods. Invited by the director of the Bochum theatre Peter Zadek to create her own version of Shakespeare's Macbeth, she found herself in a difficult situation. A large portion of her ensemble no longer wished to work with her as there was little conventional dancing in her pieces. She thus cast the Bochum guest performance with just four dancers, five actors and a singer. With this cast she was unable to deploy choreographic steps and so began by asking her performers associative questions around the themes of the play. The result of this joint investigation was premiered on 22 April 1978 in Bochum under the lengthy title He Takes Her By The Hand And Leads Her Into The Castle, The Others Follow and was almost drowned out by the storm of protest from the audience. Yet in making this unusual move, Pina Bausch had finally found the form her work would take, its dream-like, poetic imagery and bodily language justifying the worldwide success she soon achieved. In taking people's essential emotions as its starting point - their fears and needs, wishes and desires - the Tanztheater Wuppertal was not only able to be understood throughout the world, it sparked an international choreographic revolution. The secret of this success may lie in the fact that Pina Bausch's dance theatre risks taking an unflinching look at reality, yet at the same time invites us to dream. It takes the spectators' everyday lives seriously yet at the same time buoys up their hopes that everything can change for the better. For their part, they are required to take responsibility themselves. All the men and women in Pina Bausch's pieces can do is test out, with the utmost precision and honesty, what brings each and every one closer to happiness, and what pushes them further from it; they cannot offer a panacea. They always, however, leave their public in the certainty that - despite all its ups and downs - they will survive life.
In January 1980 Pina Bausch's long-term life partner Rolf Borzik died. In the early days his stage sets and costumes had largely shaped the appearance of dance theatre. Following his death his work was continued by Peter Pabst (sets) and Marion Cito (costume). The spaces created are poetic, with the outside often brought in, the stage expanded into a landscape. And the spaces are physical, affecting the dancers' movements. Water and rain allow the body to be seen through the clothes; earth makes every movement a feat of strength; the dancers' steps are traced in a layer of fallen leaves. The spaces' variety ranges from nineteenth century interiors to bare wooden boards of Japanese minimalism. The costumes too, can be as elegant as they are absurd, from the refinement of evening dress to the childish delight in dressing up. Like the pieces themselves, stages sets and costume reflect everyday life yet continually exceed it, ascending into dream-like beauty and weightlessness. The humour and the beauty, often overlooked in the beginning, even when they lay in the apparently ugly, were gradually understood over the years. Slowly it became clear what dance theatre was about; not provocation, but, in Pina Bausch's own words, 'a space where we can encounter each other'.
The worldwide development of dance theatre resulted in many international co-productions for the Tanztheater Wuppertal: Viktor, Palermo Palermo and O Dido in Italy, Tanzabend II in Madrid, Ein Trauerspiel in Vienna, Nur Du (Only You) in Los Angeles, Der Fensterputzer (The Window Washer) in Hong Kong, Masurca Fogo in Lisbon, Wiesenland in Budapest, Água in Brazil, Nefés in Istanbul, Ten Chi in Tokyo, Rough Cut in Seoul, Bamboo Blues in India and most recently the new 2009 production in Chile, which Pina Bausch was no longer able to give a title to. The work, once controversial, eventually developed into a world theatre, which can incorporate all cultural colourations and treats every person with the same respect. It is a theatre that does not aim to preach, instead creating an elemental experience of life, which each spectator is invited to participate in along with the dancers. This global theatre is generous, relaxed in its perception of the world and thoroughly charming towards its audience. It invites them to make peace with life, and trust their courage to go on living and their own strength. A mediator between cultures, it is a messenger of freedom and mutual understanding. It is a theatre which remains free of all ideology and dogma, viewing the world with as little prejudice as possible and acknowledging life – in all its facets. Out of the finds brought back from the journey which begins with each new piece, out of the many small scenes and the many dancers – ever more over the years – a global image of enormous complexity is pieced together, full of surprising turns. The Tanztheater Wuppertal has no obligations other than to human beings and thus to a humanism which recognises no borders.
Pina Bausch has been awarded many prizes and accolades for her work, including the New York Bessie Award in 1984, the German Dance Prize in 1995, the Berlin Theatre Prize in 1997, Japan's Praemium Imperiale in 1999, Monte Carlo's Nijinsky Prize, the Golden Mask in Moscow in 2005 and the Goethe Prize of the city of Frankfurt in 2008. In June 2007 she was presented with the Venice Biennale Golden Lion for her life's work and in November that year she was awarded the highly respected Kyoto Prize. In 1997 the German government honoured her with the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany, the French with the title Commandeur de l'Ordre des Arts et de Lettre in 1991 and Chevalier de la Légion d'Honneur in 2003. Several universities have awarded her an honorary doctorate.
On 30 June 2009 Pina Bausch's life journey reached its end. She will be remembered as one of the most significant choreographers of the twentieth century.
Text by Norbert Servos
Translated by Steph Morris